Step 4: Apply Ice or Cold Compress
- Sucking on ice chips can numb the area and reduce swelling.
- Caution: Avoid chewing ice to prevent further injury.
Step 5: Use Over-the-Counter Medications
- Topical oral gels like benzocaine can numb pain.
- Antiseptic mouth rinses may prevent infection.
Step 6: Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet
- Increase intake of B vitamins, iron, and folate through fruits, leafy greens, and supplements (if needed).
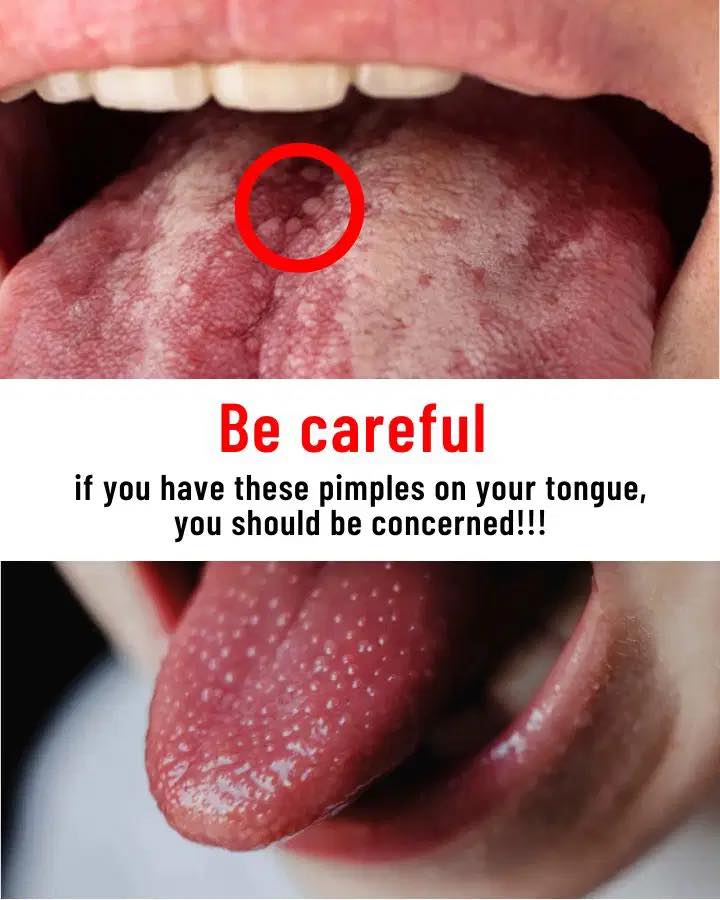
🚨 When to Be Concerned and See a Doctor
You should not ignore tongue pimples if:
- They last more than 7–10 days.
- The pain is severe or worsening.
- You notice bleeding, pus, or a foul odor.
- You have difficulty eating, swallowing, or speaking.
- You develop fever or swollen lymph nodes.
- The bumps return frequently without clear cause.
- There’s a hard lump or discolored patch that doesn’t go away—this could be an early sign of oral cancer (rare, but serious).
🩻 Diagnosis and Medical Treatment
A healthcare provider may:
- Inspect your mouth and ask about symptoms.
- Conduct swabs or blood tests to rule out infections or deficiencies.
- Prescribe antifungal, antiviral, or antibiotic medications, depending on the cause.
- Recommend biopsy if the bump is suspicious and persistent.
🛡️ Prevention Tips
- Practice consistent oral hygiene.
- Stay hydrated.
- Avoid smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Reduce stress (which can trigger canker sores and inflammation).
- Replace old toothbrushes regularly.
📝 Final Thoughts
While pimples on the tongue are often benign, they can also be signals from your body that something isn’t right. Understanding their appearance, causes, and treatments can help you take appropriate action early. Always listen to your body—if the bumps don’t resolve or if other concerning symptoms appear, seek medical advice without delay.
Your tongue is a window to your health. Don’t ignore its signals.









